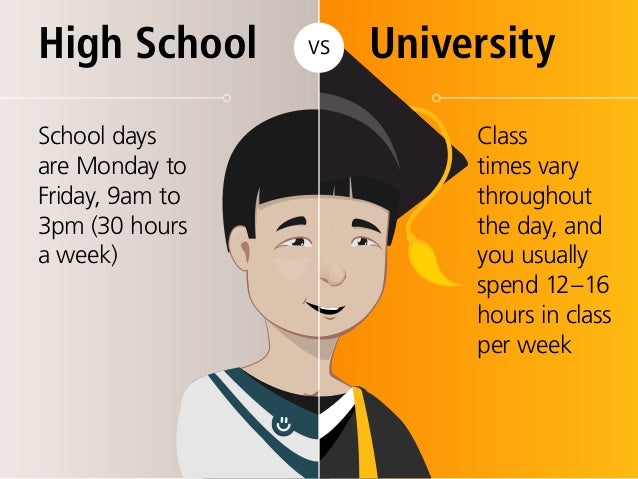
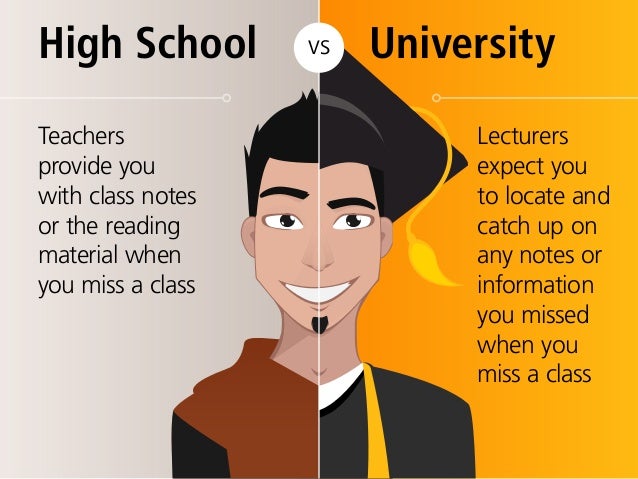
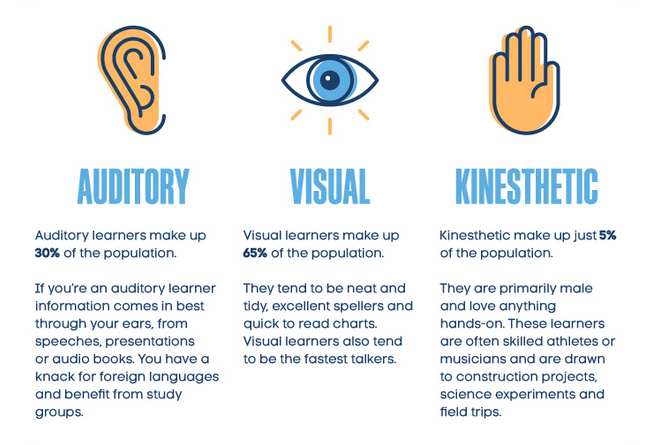
Why take notes in class?
- Organized notes will help you identify the core of important ideas in the lecture.
- A permanent record will help you to learn and remember later.
- The lecture may contain information not available anywhere else and maybe only your chance to learn it.
- Lecture is where you learn what your instructor thinks is important, and he makes up the exams.
- Class assignments are usually given in the lecture.
- The underlying organization and purpose of the lecture will become clear through note taking.
Taking the notes class: A brief summary
1. Before the lecture begins
- Make some preparations for the lecture so that you will be more likely to predict the organization of the lecture.
- Sit as near to the front of the room as possible to eliminate distractions.
- Copy everything on the blackboard and transparencies, especially the outline.
- Have a proper attitude. Listening well is a matter of paying close attention. Be prepared to be open-minded to what the lecturer may say even through you may disagree with it.
2. During the lecture
- Have your lecture paper and pencil or pen ready.
- Write down the title of the lecture, the name of the course and the date.
- Watch the speaker carefully.
- Listen carefully to the lecturer. By knowing the outline, you will be better prepared to anticipate what notes you will need to take.
- Be brief in your note taking. Summarize your notes in your own words, not the instuctor's.
- Try to recognize main ideas by signal words that indicate something important is to follow.
- Jot down details or examples that support the main ideas.
- If there is a summary at the end of the lecture, pay close attention to it.
- Ask questions about points you did not understand.
- Don't be in a rush. Be attentive, listen and take notes right up to the point at which the instructor dismisses you.
3. After the lecture
- Revise your notes as quickly as possible, preferably immediately after the lecture since at that time you will still remember a good deal of the lecture.
- During the first review period after the lecture, coordinate reading and lecture notes.
- Review your lecture notes at lease once a week and before the next lecture.
Tips on taking notes
- Collect notes for each course in one place, in a separate notebook or section of a notebook.
- Write notes on one side of the page only.
- Use a loose-leaf notebook rather than a notebook with a permanent binding. See the pattern of a lecture by spreading out the pages.
- Write name and date of the class on the first sheet for each lecture.
- Use 8 1/2 X 11 sheets of paper for your notes. This size will allow you to indent and see the structure of your notes.
- Do not perform manual activities which will detract from taking notes. Do not doodle or play with your pen. These activities break eye contact and concentration.
- Enter your notes legibly because it saves time. Make them clear.
- Use abbreviations.
- Box assignments and suggested books so you can identify them quickly.
- Mark ideas which the lecture emphasizes with an arrow or some special symbol.
- Pay close attention to transitional words, phrases, and sentences which signal the end of one idea and the beginning of another.
- Take down examples and sketches which the lecturer presents.
- Review your notes as soon as possible. Read through the notes and improve the organization if necessary.
- Listening and note taking are skills. The more you practice these techniques, the more skilled you will become.
Note-taking exercise using the Cornell Method
1. Cornell Note Taking
2. Two column method

3. Outlining method
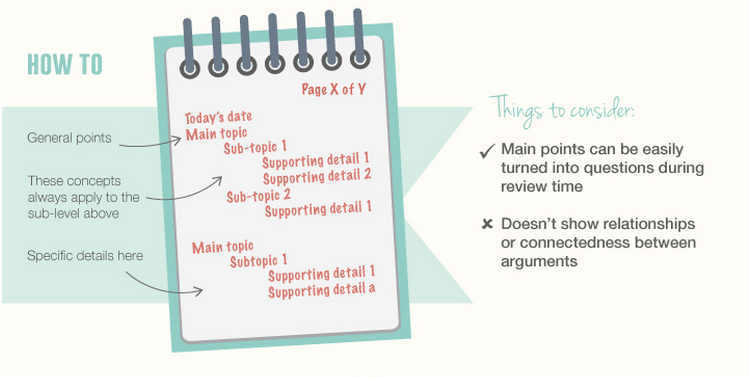

4. Mapping method

TOPIC 7: ACADEMIC INTEGRITY & PERFORMANCE
Plagiarism
Copying another person's ideas, words or writing and pretending that they are one's own work. It can involve violating copyright laws. College students who are caught plagiarizing can be expelled from school or college. It can permanently damage a student's reputation. Writers who plagiarize commit serious legal and ethical violations.
Types of plagiarism:
- Direct Plagiarism: copying and pasting someone else's work, or making minor changes to someone else's work to pass it off as their own.
- Self-Plagiarism: happens when a student submits all or part of their own previous work without permission from all involved professors.
- Mosaic Plagiarism: or called "patch writing", is when parts of other works are copied without using quotation marks. It also can be when a student keeps the same structure and meaning of an original passage and synonym.
- Accidental Plagiarism: this can happen when a student does not cite their sources. It also can be happen when a student paraphrases information without giving attributing.
How to prevent plagiarism:
- Start early
- Cite correctly
- Proofread
- Quote
- Paraphrase
- Add value
- Plagiarism checker
- Reference page
- Ask your lecturer
- Internet is a source
Calculating GPA
GPA (Grade Point Average), is a number that indicates how well or how high you scored in your scored in your courses on average. It’s meant to score you (usually on a GPA scale between 1.0 and 4.0) during your studies and shows whether your overall grades have been high or low.

CGPA
Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA), the GPA of a student that he has obtained in college or university, in the courses that he has taken. To arrive at CGPA, grade points obtained by a student in all semesters are added and divided by the sum of his total credit hours.
GPA Calculation
Failure & Dismissal

Assessment
- Calculate the GPA for first semester:
CHM138 - (A , 4.00 x 3.0)
CSC134 - (B , 3.00 x 3.0)
CTU101 - (A- , 3.67 x 2.0)
ELC121 - (B+ , 3.33 x 3.0)
MAT133 - (A- , 3.67 x 3.0)
MIC102 - (B+ , 3.33 x 3.0)
(12.00 + 9.00 + 7.34 + 9.99 + 11.01 + 9.99 = 58.33) / 17
= 3.49